[알고리즘] C 간단한 해시 알고리즘(체이닝) - 숫자
숫자 입력 시 삽입, 검색, 삭제, 현재 테이블 보기 기능 구현
구현을 하면서 충돌이 발생할 경우 체이닝을 통하여 리스트로 만들었다.
소스코드
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define BUCKET_SIZE 10
struct bucket* hashTable = NULL;
struct node {
int key;
int value;
struct node* next;
};
struct bucket {
struct node* head;
int count;
};
struct node* createNode(int key, int value) {
struct node* newNode = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->key = key;
newNode->value = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
int createHash(int key) {
return key % BUCKET_SIZE;
}
void add(int key, int value) {
int hashIndex = createHash(key);
struct node* newNode = createNode(key, value);
if(hashTable[hashIndex].count == 0) {
hashTable[hashIndex].count = 1;
hashTable[hashIndex].head = newNode;
} else {
newNode->next = hashTable[hashIndex].head;
hashTable[hashIndex].head = newNode;
hashTable[hashIndex].count++;
}
}
void remove_key(int key) {
int hashIndex = createHash(key);
int flag = 0;
struct node* node;
struct node* beforeNode;
node = hashTable[hashIndex].head;
while(node != NULL) {
if(node->key == key) {
if(node == hashTable[hashIndex].head) {
hashTable[hashIndex].head = node->next;
} else {
beforeNode->next = node->next;
}
hashTable[hashIndex].count--;
free(node);
flag = 1;
}
beforeNode = node;
node = node->next;
}
if(flag == 1) {
printf("\n [%d]가 삭제되었습니다.\n", key);
} else {
printf("\n [%d]가 존재하지 않아 삭제하지 못했습니다.\n", key);
}
}
void search(int key) {
int hashIndex = createHash(key);
struct node* node = hashTable[hashIndex].head;
int flag = 0;
while(node != NULL) {
if(node->key == key) {
flag = 1;
break;
}
node = node->next;
}
if(flag == 1) {
printf("\n 키는 [%d], 값은 [%d]입니다\n", node->key, node->value);
} else {
printf("\n 존재 하지 않는 키는 찾을 수 없습니다. \n");
}
}
void display() {
struct node* node;
printf("\n");
for(int i = 0; i < BUCKET_SIZE; i++) {
node = hashTable[i].head;
printf("Bucket[%d] : ", i);
while(node != NULL) {
printf("(key : %d, val : %d)", node->key, node->value);
node = node->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
hashTable = (struct bucket*)malloc(BUCKET_SIZE * sizeof(struct bucket));
while(1) {
printf("1.삽입 2. 검색 3.삭제 4.전체보기 : ");
int input, key, value;
scanf("%d", &input);
switch(input) {
case 1:
scanf("%d %d", &key, &value);
add(key, value);
break;
case 2:
scanf("%d", &key);
search(key);
break;
case 3:
scanf("%d", &key);
remove_key(key);
break;
case 4:
display();
break;
}
}
}
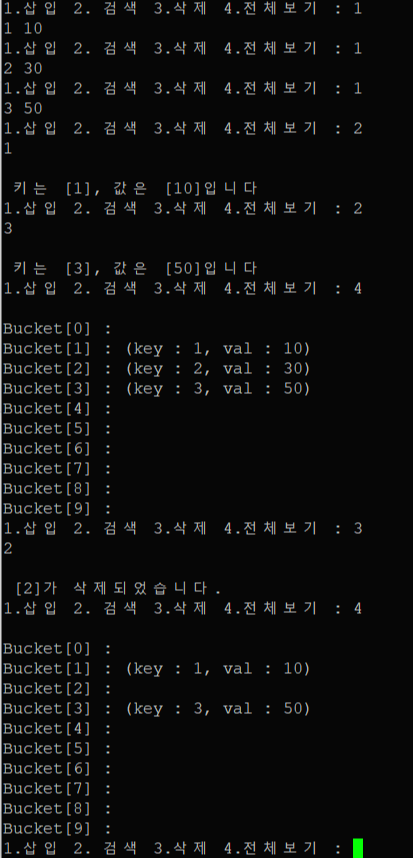
출력 결과